Ackermann Drive Simulation
By Shashank Rajiv Moghe
Note: This writeup was copied from my old website, which no is longer functional.
The challenge is to get a cone following algorithm to be implemented using just a normal RGB camera. The competition this was made for is the same as SolarMobil. I used the linearity of the relation of area occupied on screen vs. the distance of the object. I get a representation of the distance here rather than the actual physical distance with this method. The scikit-spatial library is a huge help as it simplifies a lot of the involved mathematics.
A brief overview of the steps in the algorithm:
- Pre-process image to get contours
- Filter contours to get useful data
- Fit rectangle on contour, break up badly shaped contours
- Get 3D relation from scaling areas of rectangles
- Find best fit line with individual leftward and rightward bias (approximate cone line direction locally)
- Project onto xy plane for intersection point and use depth data to find directions of vectors
- Smooth out intersection with a window filter to get goal
- Software control through PID loop
- Execute commands on robot
For the cone follower code check this file. While the simulation work has been complete, the implementation is not yet done. Check out the repository on GitHub for the code.
GitHub: Macavitycode/Cone-follower
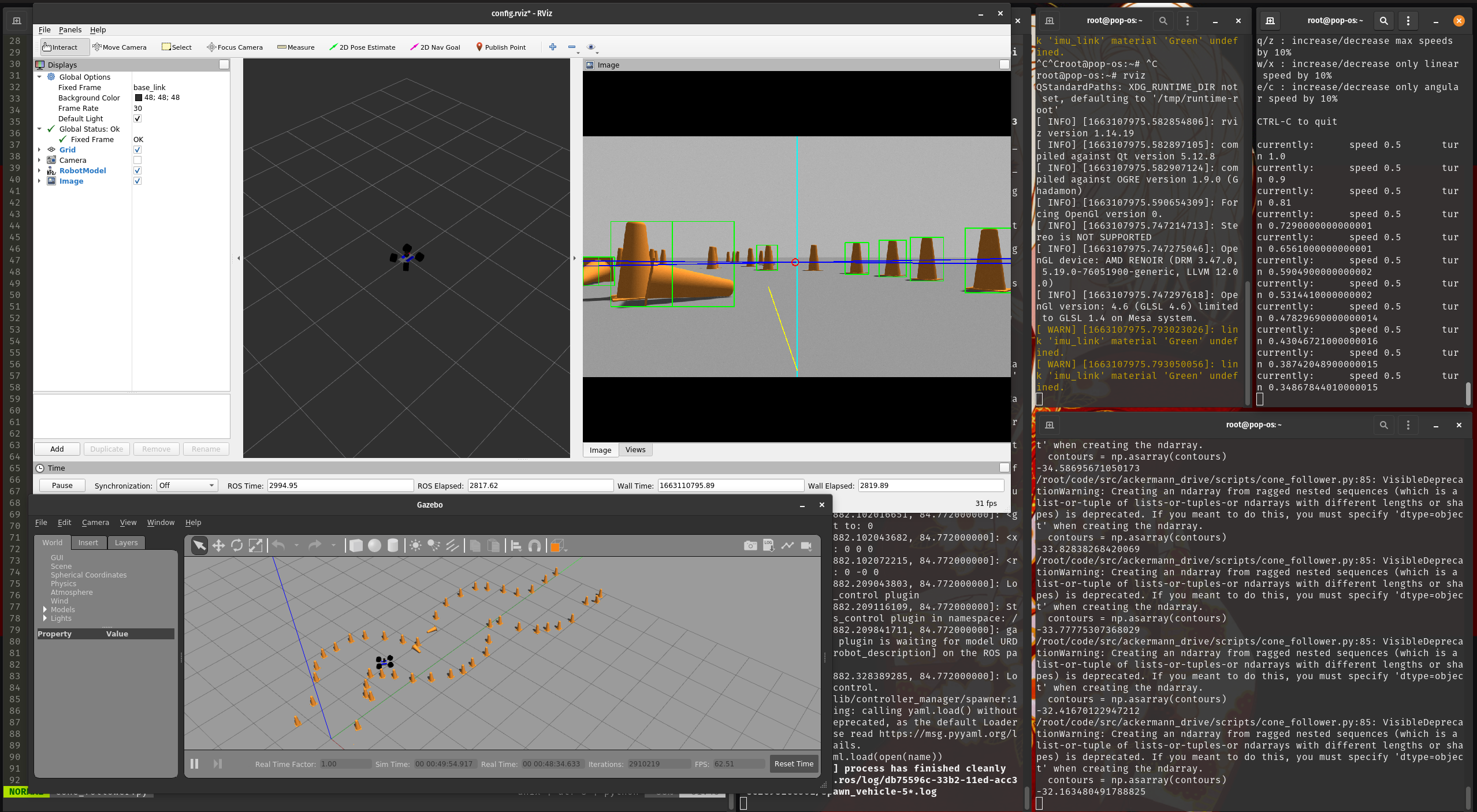
The gazebo simulation on the bottom left shows the environment. The rviz window is showing the contours (green), cone tracking lines (blue), screen centerline (light blue), point of intersection (red circle) and direction vector to move in (yellow).